Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Reading NEXRAD Data from the AWS Cloud#
Within this example, we show how you can remotely access Next Generation Weather Radar (NEXRAD) Data from Amazon Web Services and plot quick looks of the datasets.
print(__doc__)
# Author: Max Grover (mgrover@anl.gov)
# License: BSD 3 clause
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pyart
Read NEXRAD Level 2 Data#
Let’s start first with NEXRAD Level 2 data, which is ground-based radar data collected by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), as a part of the National Weather Service ### Configure our Filepath for NEXRAD Level 2 Data We will access data from the noaa-nexrad-level2 bucket, with the data organized as:
s3://noaa-nexrad-level2/year/month/date/radarsite/{radarsite}{year}{month}{date}_{hour}{minute}{second}_V06
Where in our case, we are using a sample data file from Houston, Texas (KHGX) on March 22, 2022, at 1201:25 UTC. This means our path would look like:
aws_nexrad_level2_file = (
"s3://noaa-nexrad-level2/2022/03/22/KHGX/KHGX20220322_120125_V06"
)
We can use the pyart.io.read_nexrad_archive module to access our data, passing in the filepath.
radar = pyart.io.read_nexrad_archive(aws_nexrad_level2_file)
Let’s take a look at a summary of what fields are available.
list(radar.fields)
['velocity', 'spectrum_width', 'cross_correlation_ratio', 'reflectivity', 'differential_phase', 'differential_reflectivity']
Let’s plot the reflectivity/velocity fields as a first step to investigating our dataset.
Note: the reflectivity and velocity fields are in different sweeps, so we will need to specify which sweep to plot in each plot.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
display = pyart.graph.RadarMapDisplay(radar)
ax = plt.subplot(121, projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())
display.plot_ppi_map(
"reflectivity",
sweep=0,
ax=ax,
colorbar_label="Equivalent Relectivity ($Z_{e}$) \n (dBZ)",
vmin=-20,
vmax=60,
)
ax = plt.subplot(122, projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())
display.plot_ppi_map(
"velocity",
sweep=1,
ax=ax,
colorbar_label="Radial Velocity ($V_{r}$) \n (m/s)",
vmin=-70,
vmax=70,
)
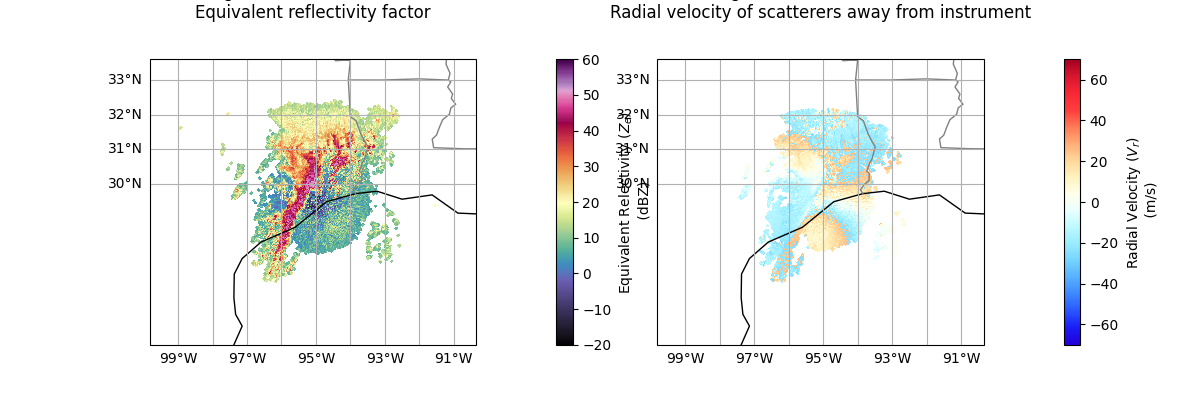
Within this plot, we see that the velocity data still has regions that are folded, indicating the dataset has not yet been dealiased.
Read NEXRAD Level 3 Data#
We can also access NEXRAD Level 3 data using Py-ART!
These datasets have had additional data quality processes applied, including dealiasing.
Each Level 3 data field is stored in separate file - in this example, we will look at the reflectivity and velocity field at the lowest levels. These correspond to the following variable names:
N0U- Velocity at the lowest levelNOQ- Reflectivity at the lowest level
These datasets are also in a different bucket (unidata-nexrad-level3), and the files are in a flat directory structure using the following naming convention:
s3://unidata-nexrad-level3/{radarsite}_{field}_{year}_{month}_{date}_{hour}_{minute}_{second}
For example, we can look at data from that same time as the NEXRAD Level 2 data used previously (March 22, 2022 at 1201 UTC)
aws_nexrad_level3_velocity_file = (
"s3://unidata-nexrad-level3/HGX_N0U_2022_03_22_12_01_25"
)
aws_nexrad_level3_reflectivity_file = (
"s3://unidata-nexrad-level3/HGX_N0Q_2022_03_22_12_01_25"
)
Read our Data using pyart.io.read_nexrad_level3
radar_level3_velocity = pyart.io.read_nexrad_level3(aws_nexrad_level3_velocity_file)
radar_level3_reflectivity = pyart.io.read_nexrad_level3(
aws_nexrad_level3_reflectivity_file
)
Let’s confirm that each radar object has a single field:
print(
"velocity radar object: ",
list(radar_level3_velocity.fields),
"reflectivity radar object: ",
list(radar_level3_reflectivity.fields),
)
velocity radar object: ['velocity'] reflectivity radar object: ['reflectivity']
Plot a Quick Look of our NEXRAD Level 3 Data
Let’s plot the reflectivity/velocity fields as a first step to investigating our dataset.
Note: the reflectivity and velocity fields are in different radars, so we need to setup different displays.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
reflectivity_display = pyart.graph.RadarMapDisplay(radar_level3_reflectivity)
ax = plt.subplot(121, projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())
reflectivity_display.plot_ppi_map(
"reflectivity",
ax=ax,
colorbar_label="Equivalent Relectivity ($Z_{e}$) \n (dBZ)",
vmin=-20,
vmax=60,
)
velocity_display = pyart.graph.RadarMapDisplay(radar_level3_velocity)
ax = plt.subplot(122, projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())
velocity_display.plot_ppi_map(
"velocity",
ax=ax,
colorbar_label="Radial Velocity ($V_{r}$) \n (m/s)",
vmin=-70,
vmax=70,
)
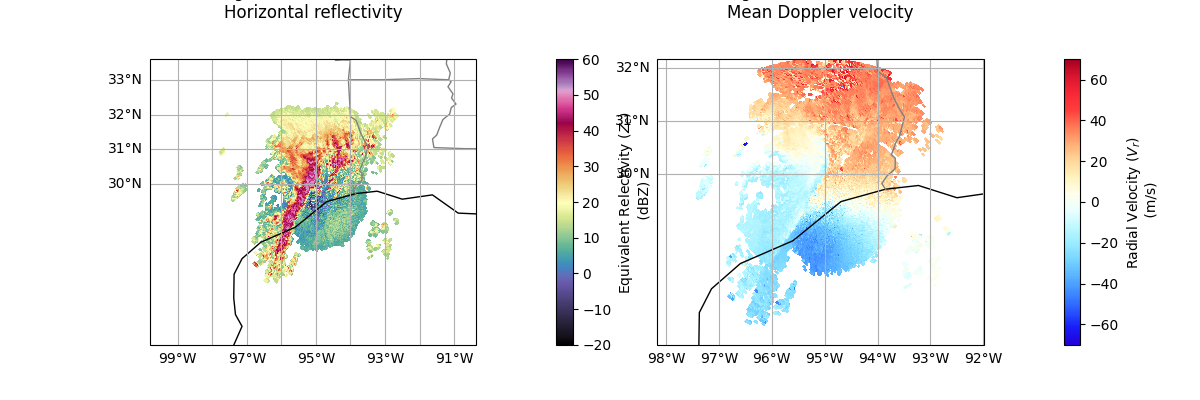
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 22.440 seconds)